There are a lot of health benefits of going on a high-protein low-carb diet, and this guide will tell you everything you need to know!
You’ll discover how much protein you need, are high protein diets dangerous, which are the best high-protein snacks, how to eat protein at every meal, and the amazing benefits of increasing your protein rather than your fat.

If you are new here, you may want to read the keto glossary to help you understand keto words, keto acronyms, and keto slang.
If you want to try the protein-sparing modified fast (PSMF diet), you can download the free printable PDF guidebook, meal plan, PSMF food list, and PSMF calculator.
What is protein?
Protein supplies the body with essential amino acids. Your body needs protein for the building blocks for growth and development. Protein is also required to build and repair bone, muscles, aids tissue repair, play a part in your immune system, promotes healthy hair, skin, and nails, cuts cravings, and aids healing.
Are you ready to create the ultimate 12-month blueprint for reaching your health & weight loss goals this coming year?

Our free on-demand video training will walk you through how to make 2024 THE year you set health goals…and keep them.
Why is important to eat plenty of protein? Because protein under-consumption INCREASES appetite to ensure sufficient intake of essential amino acids.
How much protein do you need?
Minimum protein intake: for a 70kg sedentary women = 0.8g/kg (0.36g/pound) = 56g protein per day.
High protein diet: for a 70kg sedentary women = 1.5g – 2g/kg = 105g – 140g protein per day.
How much protein should you eat at each meal?
If you want to eat 30g protein at each meal with some high-protein snacks, your day could look like this.
Breakfast: 3 boiled eggs (18g) with 3 small slices of bacon (12g)
Lunch: Chicken Caesar salad (21g) followed by Greek yogurt (9g).
Dinner: 2 beef patties (24g) with a fried egg (6g) and coleslaw.
Snacks: 3 slices turkey (18g), a small can of tuna (12g), a handful of walnuts (5g), cubes of cheese (7g).
What are macronutrients?
Food is made up of protein, carbohydrates, fat, and water. Just by adjusting the ratio of your macronutrients, you can be on a keto diet, low-fat diet, low-calorie diet, low-carb diet, high protein diet, or fat-free diet.
When you reduce your carbs you become a fat burner, not a sugar burner. Your body will burn fat as fuel and produce ketones, hence being called the keto diet. When you burn fat, you are in nutritional ketosis.
That being said, more and more keto dieters are switching their macros up to allow for higher protein. This is called a high-protein keto diet or a high-protein low-carb diet (AKA a low-carb high-protein diet).
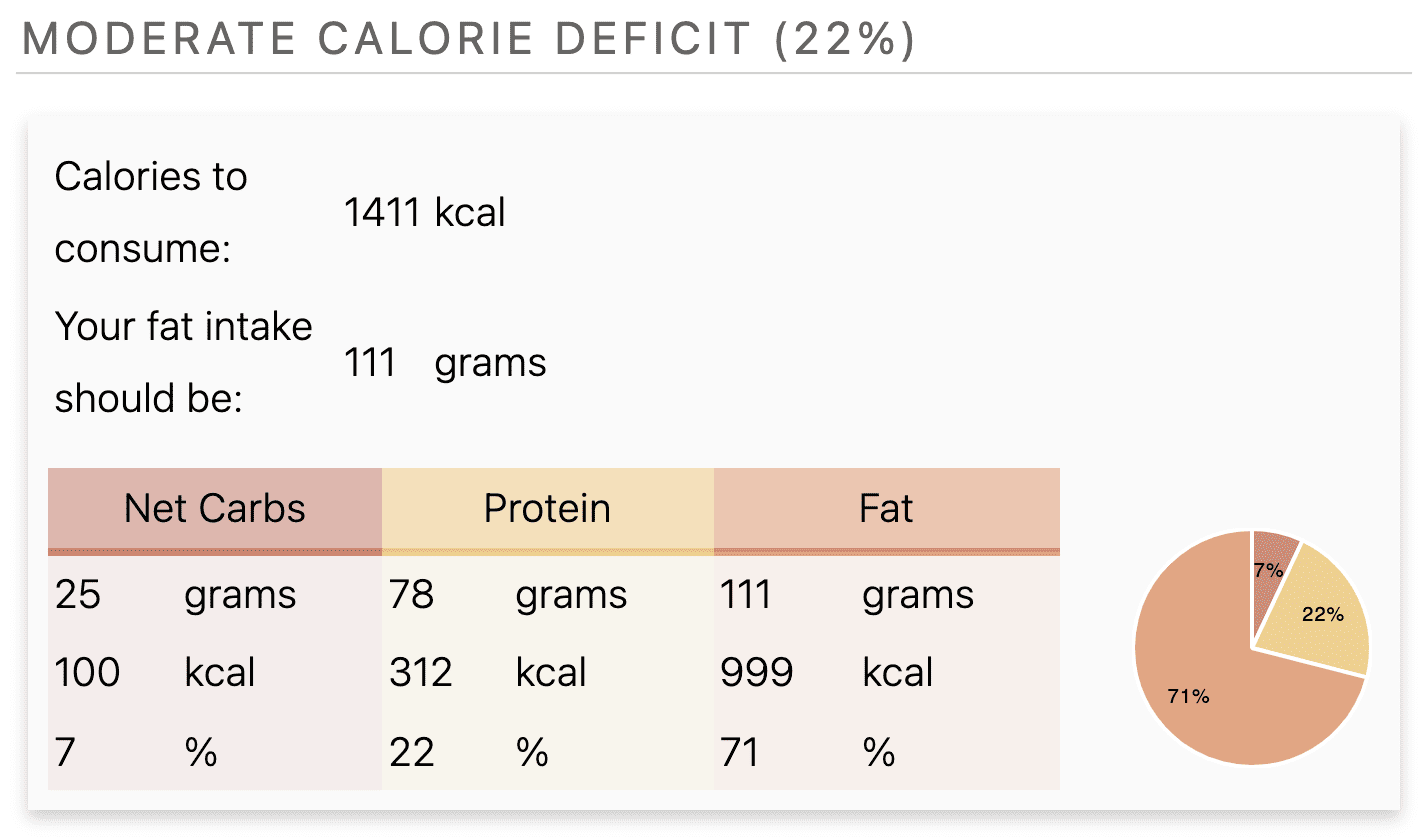
This is just one example of macronutrient ratios when you use a keto calculator.
What is a high protein diet?
If you are on a high protein diet you will reduce carbs, eat more protein, and reduce your fat.
The current minimum recommended minimum protein intake is only 0.8 g protein per kg of body weight (0.36 g per pound of body weight). This is only enough to prevent a protein deficiency and does not take into consideration your level of activity. Source.
A high protein diet ranges from 1.3 grams of protein per kg of body weight ((0.6 grams per pound) up to 3 grams of protein per kg of body weight (1.4 g per pound).
What does a high-protein dinner look like?
A high-protein low-carb dinner might be a large slice of salmon, steak, or chicken with a large salad drizzled in a little extra virgin olive oil.
A keto dinner might be a regular slice of salmon, steak, or chicken with a medium salad drizzled with plenty of mayonnaise and some cheese.
Is the keto diet a high-protein diet?
The ketogenic diet is often thought of as a high protein diet. However, keto is traditionally more moderate protein as it focuses on carb restriction and high fat to train your body to burn fat for energy instead of carbs.
People that eat high protein meals also avoid high carb foods such as potatoes, rice, wheat bread, pasta, and corn.
It isn’t so much about calorie intake as it’s about eating nutrient-rich foods that train your body to use protein and fat stores for energy.
Is it better to eat more protein (and less fat)?

The most common myth of the keto diet is that you must eat excessive fat. In fact, it is the most common mistake people make and the most common reason weight loss stops.
The keto food pyramid helps you to set your carbs (which should be a limit), protein (which is a target to reach), and fat (which is often used to control hunger).
When starting a low-carbohydrate diet, you add plenty of healthy fats to your meals and snacks but NOT to excess. Do not drink bulletproof coffees and continuously eat fat bombs.
Benefits of high protein diets
There are a lot of health benefits of eating a low carbohydrate diet that is high in protein. This all comes from controlling your appetite and food intake, eating fewer processed foods, and reducing calories by reducing fat.
Lose weight
Weight loss is one of the most popular reasons people eat a low-carb diet. As you train your body to burn body fat for energy instead of carbohydrates, you will lower your body weight.
This is good news for anyone that struggles with weight gain. High-protein low-carb diets can help you lose weight easier as both protein and fat are known to be more satiating but protein has fewer calories than fat. You will still be burning body fat (not fat from your food).
If you hit a weight loss plateau, lowering your carbs, cutting back on fat, and increasing protein might help you break it. Check out this guide to help you break a weight-loss stall.
Build muscle
Another benefit of higher protein diets is by changing your body composition by increasing muscle mass and losing weight while doing weight-bearing exercises. This is why you will see bodybuilders buying a lot of protein powder and eating a lot of grilled chicken breasts!
If your goal is to change your body composition and increase muscle growth, then eating more protein might be the answer.
Increasing muscle mass will help raise your resting metabolic rate which in turn helps maintain fat loss and improve lean body mass.
Maintain blood sugar levels
High-protein diets also help you manage blood sugar levels. You don’t necessarily have to count calories (although it can be helpful at the beginning to get an idea of what you are consuming). Instead, just eat fewer carbs and more protein.
Maintaining blood sugar control is very important for anyone that has been told they have pre-diabetes, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes. Lower blood sugar often occurs with a low-carb diet because low-carb foods help prevent blood sugar spikes. Source.
Eating more protein helps you keep full until your next meal and helps prevent continuous snacking which often keeps blood sugars elevated.
Lower risk of heart disease
One of the side benefits of reaching a healthy weight and having lean body mass is that you lower your risk for heart disease. Inflammation is the real cause of heart disease, not cholesterol (read the cholesterol myth and why cholesterol is so important for our health).
If you have high blood pressure, then reducing your carbohydrate intake and sugars have been shown to reduce blood pressure and cardiovascular risk factors such as inflammation and raised triglycerides. Source.
A high protein diet may reduce blood pressure and reduce triglycerides and inflammation which are the real cause of heart disease, not cholesterol.
Better bone health
A high protein diet is also very beneficial for your bones. The calcium from high-protein dairy is beneficial for bone growth and decreases your risk factors for osteoporosis.
However, protein actually makes up 50% of bone. Healthy bones are continually broken down then regenerated. Amino acids are needed to support bone health and bone strength across our lifetime. Source.
Some foods – like cottage cheese – are high in both protein and calcium and provide quick and easy protein power in a low-carb diet.
Protein-rich foods help promote strong healthy bones, improve calcium absorption, and could help repair bone loss and prevent osteoporosis. (Source).
How many calories are in a high protein diet?
High-protein low-carb = increase your protein and lower your carbs.
High-protein low-calorie = increase your protein and lower your fat.
Generally, we do not count calories on a low-carb keto diet, but calories do count. The source of your calories and their effect on your hormones and fat storage is vital to understand.
Nutrition values:
Carbohydrates are 4 calories per gram.
Protein is 4 calories per gram.
Fat is 9 calories per gram.
What does 100 calories look like?

100 calories from carbs – will trigger raised blood sugars, hunger, and cravings. Example 9 crisps.
100 calories from protein – will indirectly raise blood sugars moderately but keep you full and provide all the essential amino acids your body needs to function. Example small handful of prawns.
100 calories from fat – will not affect blood sugars but will keep you satiated. Example 1 tablespoon of butter.
Eating more protein keeps you fuller for longer but with fewer calories than fat. (Source).
Low-carb high-protein foods to eat
If you are looking at low-carb diets, these are the types of food that you will want to eat the most. These low-carb foods are also high in protein and will help you stay on track when you are eating high protein low carb.
How to build the perfect high-protein low-carb meal

1: Pick your protein (usually meat).
2: Pick your low-carb vegetables.
3: Add some healthy fat or high-protein dairy.
Top 10 high-protein meats

When you eat meat, you will increase your protein intake easily. That being said, not all types of animal proteins are the same. How much protein is in meat varies from animal to animal and depends on the cut of meat chosen.
Some ground beef has more fat and less protein. That’s why a lot of people prefer a combination of full-fat and lean pork and chicken on a high protein low carb diet.
- Chicken breast, skinless – 1 cup (245g) = 75.9g protein
- Chicken breast, skin eaten – 1 cup (245g) = 67.2g protein
- Salmon steak – 1 cup (245g) = 62.4g protein
- Ground beef 5% fat – 1 cup (217g) = 59.1g protein
- Ground beef 15% fat – 1 cup (217g) = 56.2g protein
- Prawns – 1 cup (245g) = 58.9g protein
- Tuna – 1 cup (227g) = 57.9g protein
- Pork roast – 1 cup (245g) = 56.7g protein
- Sirloin steak (fat eaten) – 1 cup (245g) = 56.9g protein
- Pork rinds – 1 cup (30g) = 18.4g protein
It’s also a good idea to add fatty fish like salmon to your eating plan. The omega-3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory, may help with rheumatoid arthritis, depression, lupus, migraine headache, and support brain and blood health. This Instant Pot salmon is the perfect beginner’s recipe. Source.
How to include more high-protein vegetables into your meals
There are so many ways you can get 30g of protein at each meal.
- A quick high-protein snack idea is to snack cold meat and leftover meat.
- Always order a chicken Ceasar salad instead of a regular Ceasar slsad.
- Ask for extra burger patties inside your burger.
- Use ground chicken to make a keto ABC burger.
- FInd new and exciting ways to use ground beef for dinner.
- Make quick slow-cooker salmon or Instant Pot salmon.
Top 10 high-protein fruits and vegetables

It is difficult to have a high protein intake by eating fruits and vegetables. Not all types of fruit or vegetables are beneficial on low-carb diets.
These handy protein charts will help you pick the best high-protein fruit and vegetables for a vegetarian diet.
Most fruit has minimal protein, too many carbs, and are too high in natural sugars to eat on a low-carb high-protein diet. But fruit and vegetables are low-calorie and packed with nutrition and are regularly part of a healthy diet.
Vegetables are delicious and useful to bulk up a high-protein low-carb diet. Choose low-carb vegetables and the small amount of protein they provide is just a bonus.
- Guava – 1 cup (165g) = 14.6g net carbs and 4.2g protein.
- Raspberries – 1 cup (123g) = 6.6g net carbs and 1.5g protein.
- Grapes – 1 cup (151g) = 25.8g net carbs and 1.1g protein.
- Banana – medium = 23.9g net carbs and 1.1g protein.
- Lima beans – 1 cup (188g) = 25.9g net carbs and 14.7g protein
- Soy beans – 1 cup (172g) = 3.7g net carbs and 31.3 g protein
- Green peas – 1 cup (160g) = 15.4 g net carbs and 8.2g protein
- Asparagus – 1 cup (180g) = 3.7g net carbs and 4.3g protein
- Cauliflower – 1 cup (124g) = 2.2g net carbs and 2.3g protein
- Spinach – 1 cup (30g) = 0.4g net carbs and 0.9g protein
Protein values of fruit and vegetables are minimal when compared to one small boiled egg which has 5.5g protein and only 0.5g carbs.
If you want to eat bananas, grapes, or lima beans, be careful with how many you eat. They have more than 24 grams of net carbs in each serving.
Read more about the carb count in fruit here.
How to include more high-protein vegetables into your meals
Adding more low-carb low-starch vegetables to your meal is a great way to bulk up a meal but without the extra calories and carbs. These are the most popular low-carb side dishes.
- High-protein chicken Caesar salad
- Keto Big Mac salad
- Low-carb Mexican coleslaw
- Keto cheesy baked asparagus
- Mashed cauliflower – cheesy, mustard, butter and curry
- Cauliflower couscous
Top 10 high-protein dairy

Nutrient-dense lower fat low-carb dairy helps you eat more protein without going over your total calories. High-protein low-carb dairy is so versatile and can be enjoyed in sweet or savory recipes.
Some of the most popular low-carb dairy foods are Greek yogurt or high-protein cheeses because they are high protein, low-carb, and lower in fat.
- Edam (shredded) – 1 cup (113g) = 1.6g net carbs and 28.2g protein
- Low-fat cottage cheese – 1 cup (226g) = 6.1g net carbs and 28g protein
- Cheddar (shredded) – 1 cup (113g) = 3.8g net carbs and 25.8g protein
- Non-fat Greek yoghurt – 1 cup (245g) = 8.7g net carbs and 25g protein
- Mozzarella cheese (shredded) – 1 cup (113g) = 2.8g net carbs and 24.4g protein
- Feta (crumbled) – 1 cup (150g) = 5.8g net carbs and 21.3g protein
- High-protein yoghurt – 1 cup (237g) = 5.8g net carbs and 19.5g protein
- Cream cheese (original) – 1 cup (232g) = 4.1g net carbs and 16.6g protein
- Cream cheese (low-fat) – 1 cup (232g) = 11.6g net carbs and 14.2g protein
- Heavy cream – 1 cup (238g) = 6.8g net carbs and 6.8g protein
How to include more high-protein dairy into your meals
Most low-carb diets will feature recipes that include dairy products like milk, cheese, or cream. Here are the most popular ways to eat more high-protein dairy on low-carb and keto diets:
- Add non fat Greek yoghurt to your sugar-free keto granola.
- Add reduced fat cheese (such as shredded Edam cheese) to your meals or low-carb side dishes.
- Add low-fat cottage cheese to salads or mix in some tuna and chives and eat on it’s own.
- Make low-carb creamy sauces with low-fat high-protein dairy such as sour cream.
- Create high protein desserts like mousse or cheesecake (find dozens of low-carb cheesecake recipes here!)
- Use high-protein cheese to make low carb bread (fathead dough is a personal favourite of mine).
- Chaffles are basically cheese and eggs and they can be used to replace bread on most low carb diets.
Top 10 high-protein nuts and seeds

Nuts and seeds are a source of natural fat and can help you decrease your carb intake while adding a bit of protein to your diet.
You can see which are the best high-protein and low-carb nuts to enjoy with these protein in nuts charts.
- Peanuts – 1 cup (146g) = 18.6g net carbs and 35.6g protein.
- Pumpkin seeds – 1 cup (118g) = 9.7g net carbs and 35.2g protein.
- Sunflower seeds – 1 cup (140g) = 15.9g net carbs and 29.1g protein.
- Almonds – 1 cup (130g) = 11.4g net carbs and 27.5g protein.
- Chia seeds – 1 cup (160g) = 12.4g net carbs and 26.5g protein.
- Cashews – 1 cup (130g) = 34.9g net carbs and 23.7g protein.
- Brazil nuts – 1 cup (133g) = 5.6g net carbs and 19g protein.
- Walnuts – 1 cup (117g) = 8g net carbs and 17.8g protein.
- Pecans – 1 cup (109g) = 4.6g net carbs and 10g protein.
- Macadamias – 1 cup (110g) = 5.7g net carbs and 8.7g protein.
How to include more high-protein nuts and seeds into your meals
- Nut butters make the perfect high-protein snack with almond butter providing 3.4g protein per tablespoon and peanut butter will give you 4g protein per tablespoon.
- Make low-carb gluten-free granola which is packed with low-carb seeds and nuts.
- Add sunflower seeds and olive oil to a salad. In fact, salads are a quick and easy low-carb meal that you can have on high protein diets. Don’t think that salads need to be boring, either – check out this keto hamburger salad as proof!
- Pumpkin seeds are a delicious salty snack. I also recommend sprinkling pumpkin seeds on top of soups—it works very well in this keto pumpkin soup with bacon.
- Chia seeds are another powerhouse ingredient that can amp your protein while keeping carbs low. Chia seed pudding is an easy make-ahead meal to try. You can also sprinkle chia seeds in your eggs or smoothies too.
Remember, while you may be focused on protein intake, it’s important to eat moderate healthy fats when you are eating very few carbs. This way your body will burn fat for fuel instead of carbs. Nuts and seeds are the perfect way to supplement this!
Frequently asked questions
Here are some questions people often ask about eating a high-protein low-carb diet. If you don’t see your question in this list, please leave it in the comments below.
Yes, you can lose weight on a high protein low carb diet. If you eat the correct amount of carbs and protein, you will train your body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbs. Increased protein helps you to stay fuller longer. This aids in weight loss and appetite control.
Not necessarily. While purists will say keto is a moderate protein diet, that focuses on eating fat and ultra-low-carb, many of my Ditch The Carbs PRO members have found upping their protein intake to kick start weight loss again and help them reach their ideal body weight (without being hungry).
There is some debate about whether eating too much protein can indirectly increase blood sugars and lower your body’s ketone creation, but that can vary from individual to individual.
The best way to see if the protein is aiding you in your keto goals is to test and see. Here are the three best methods to check ketones!
What’s more dangerous is a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugar that causes inflammation, chronic high blood sugars, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
If you are on a high-protein diet, then you should avoid eating refined carbohydrates. These are high-carb foods that have been stripped of their fiber and nutrients. Examples include cakes, cookies, white bread, white rice, white pasta, and sugary breakfast cereal.
It depends. If you ask 10 medical experts you will get 10 different answers. But all experts agree that the studies on protein and kidney disease are unreliable and it’s actually the high-carb and high-sugar diet that is more dangerous to kidney health. Source (1). (2)
No, a high protein diet is not the same as a low-fat diet. In fact, you will probably eat more healthy fats on a low-carb diet.
That is because instead of unhealthy fats and oils, you will be consuming healthy fats from salmon, nuts, and seeds. Do not be afraid of how much fat you eat, just make sure you are eating the correct kind.
To eat 30g of protein you need to eat 1.1 cups cheese, 0.6 cup prawns, 0.4 cup chicken, 0.5 cup salmon, 15 cups of cauliflower, or 35 cups of spinach. See more protein charts here.
The easiest way is to enjoy 3 boiled eggs (18g) with 3 small slices of bacon (12g).
Or you could eat 5 eggs, a high-protein yogurt and low-carb granola, a protein chia breakfast puddings, or half a cup of leftover chicken, steak, or other cold meat.
You might also want to take a look at the best high-protein breakfast ideas (that will keep you full). They are delicious and perfect for breakfast meal prep.
No, one medium banana has only 1.3 grams of protein and 25-30g carbs.
The Atkins diet is another example of a diet that asks you to lower your carbohydrate intake while increasing your protein but it is not traditionally a high-protein diet. The Atkins diet does not base its eating plan around nutrient-dense foods, but instead relies on low-carb bars to help weight loss on a low-carb diet.
Protein shakes added into a low-carb diet are an easy solution if you are a low-carb vegetarian or a keto vegan and find it difficult to reach your protein targets.
Protein powders are also useful if you don’t want to cook and don’t want to meal prep. Protein shakes are commonly used by bodybuilders who want to increase their muscle mass while weight lifting.
But, protein powders are often highly processed, high in sugar, and don’t provide all the whole food nutrition that real food does. If you rely on protein shakes and protein bars for your meals, you are said to be on a lazy keto diet (dirty keto).

Related posts
Get our FREE guide to finally fix your metabolism!
Losing weight & getting healthy is never easy, but lately you might feel like it’s suddenly become impossible.
Our Flip the Switch guide will help you clearly understand what’s been going on, as well as exactly what you can do to get your metabolism working again so that you can look and feel your best—it’s easier and more simple than you think!






















Hi Libby. I am wondering why fried eggs are not recommended? I fry mine is a bit of olive oil.
Yes, you can have fried eggs, I have 3 fried eggs when I do eat breakfast and even sometimes for a quick and easy lunch. 3 large eggs have 18g protein.